Since the internet is vital to global progress, cybersecurity has never been more difficult or crucial. Fast-developing technology and smarter threats have pushed organizations to the brink of chaos, revealing weaknesses in even the strongest systems. Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) are the foundation of modern cybersecurity strategies.
GRC is a basic way for an organization to ensure its policies meet regulatory standards, find and reduce risks, and follow the rules. When these three things work together, businesses can confidently protect their digital assets and reputations.
Table of Contents
Understanding GRC in Cybersecurity
What is GRC in Cybersecurity?
In the ever-changing field of cybersecurity, where threats change as quickly as the technologies used to stop them, GRC is a key part of strong digital defense. It consists of three important parts: Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance. These parts work together to create a unified strategy that helps companies protect their assets, follow the rules, and manage risks.
Governance provides the framework for security policies and ensures that everyone is held accountable and that decisions are in line with the organization’s goals. Risk management finds, evaluates, and reduces potential threats to prevent weaknesses. Finally, compliance ensures that all regulatory standards, from GDPR to HIPAA, are followed to avoid fines and damage.
Governance is the compass, risk management is the shield, and compliance is the rulebook. They must work together to navigate and protect against an ever-changing threat landscape. If they don’t, organizations risk becoming inefficient and vulnerable to breaches and regulator fines.
The Evolution of GRC
To understand how important GRC is in cybersecurity, you must know how it was created. GRC was originally created as a tool for managing corporate governance and financial risk, but it has evolved to meet the needs of today’s businesses. As companies went digital and cyber threats increased, they needed a framework that covered governance, risk, and compliance.
GRC began with paper-based compliance checklists and separate risk assessments, but as cyberattacks became more common and targeted data centers and endpoints, organizations realized how important cybersecurity was and created cybersecurity-specific GRC frameworks.
With global standards like ISO 27001 and frameworks like NIST, GRC has become a complex ecosystem that helps organizations manage internal processes and protect themselves from external threats. Modern GRC tools use AI, machine learning, and automation to make governance easier, monitor risks, and ensure real-time compliance.
GRC in cybersecurity is now both operational and strategic. As the digital frontier grows, GRC evolves to keep firms adaptable, robust, and ready for tomorrow’s threats.
The Importance of GRC in Cybersecurity
Why is GRC Crucial in Cybersecurity?
GRC (Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance) is a key part of resilience in today’s connected digital world, where cyber threats are changing quickly. By combining these three pillars, companies can take a proactive and structured approach to risk management while still following stricter rules.
Governance sets clear rules for who is responsible for what, while risk management finds weaknesses, determines how they might affect things, and finds ways to fix them. Compliance ensures that complicated rules like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS are followed, which can be confusing but necessary to maintain trust and avoid huge fines.
GRC, when properly implemented, can prevent data breaches, large fines, and irreparable reputation damage. For instance, a global retailer could be fined millions of dollars for GDPR violations, or a healthcare provider could be crippled by a ransomware attack caused by poor risk management.
Real-World Impacts of GRC in Cybersecurity
A financial institution faced rising cyber threats. Using a customized GRC framework, the organization was able to find possible attack vectors, put in place protective measures, and meet strict regulatory requirements, resulting in a 40% drop in security incidents and a smooth audit process that earned stakeholder trust.
According to a 2023 study, companies with mature GRC frameworks had 60% fewer cybersecurity incidents than those without. Another survey found that compliance violations cost companies an average of $4.6 million per breach, demonstrating the dangers of ignoring GRC.
More than just a framework, GRC frameworks help businesses in manufacturing, healthcare, and technology stay ahead of new threats and adapt to changing regulations. They are a lifeline that connects strategy, execution, and accountability.
Components of GRC in Cybersecurity
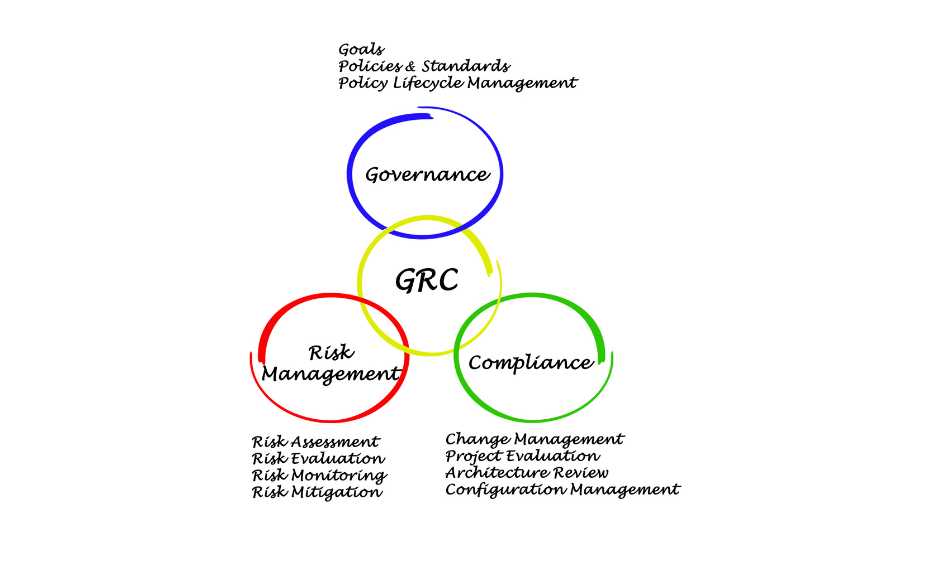
Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) are the most crucial parts of a strong defense strategy because cybersecurity is always changing. Each pillar has its own role, but when they work together, they make an organization safer. Let us examine these parts in detail, combining complexity with useful information.
Governance
Governance is the framework that governs cybersecurity decisions, policies, and roles. It guides an organization’s security efforts and ensures that every action meets goals and government requirements.
Governance is like a skyscraper’s plan: it determines the structure, ensures stability, and prepares for long-term growth. Without governance, cybersecurity efforts risk disorganization, reaction, and failure.
Governance determines who is responsible for protecting sensitive data, how decisions are made, and which protocols must be followed. However, strong governance also requires leaders to make cybersecurity a priority and part of the organization’s culture. Accountability starts at the top and spreads to all employees, cont.
Governance makes decisions happen in the real world, whether it is a data protection policy or a breach response plan. It ensures that actions are organized, uniform, and most importantly, effective.
Risk Management
Risk management—finding, assessing, and decreasing cyber hazards before they become crises—is smart and required because data breaches, ransomware attacks, and insider threats are so widespread.
First, list all the risks. Which systems are weakest and which threats are most likely to exploit them? Next, businesses must consider how these risks might affect them financially, operationally, and reputationally. Risk assessment frameworks like ISO 27001 and NIST help group and rank threats.
Modern risk management relies on advanced analytics platforms, automated monitoring systems, and predictive algorithms to provide real-time information to prevent threats or respond quickly.
As technology changes, new vulnerabilities appear, therefore risk management must be examined and updated constantly. Companies that can master this cycle will be successful cybersecurity warriors.
Compliance
Compliance, the third part of GRC, ensures that businesses follow laws, rules, and ethics. Once governance decides what to do and risk management handles threats, compliance ensures that everything done meets internal and external responsibilities.
GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA have strict rules about how data can be collected, stored, and shared. If an organization violates these rules, it could face huge fines and reputation damage that could destroy its credibility.
Compliance includes making doing the right thing a habit and passing audits to ensure processes comply with the law.
Consider a healthcare organization that keeps patient records. Compliance ensures that they are encrypted, that only authorized staff can access them, and that there are procedures to handle breaches. It is not just about avoiding fines; it is about saving lives.
Compliance impacts ethics, shareholder trust, and cybersecurity. In a time of increased scrutiny, firms that prioritize compliance show they value transparency, accountability, and honesty.
Synergy of GRC Components
GRC is important because governance sets the vision, risk management manages threats, and compliance enforces rules. Together, they create a stronger cybersecurity strategy.
By carefully using these pieces, organizations may strengthen their defenses, decrease risks, and establish trust in a more linked digital environment.
Implementing GRC in Your Organization
Steps to Implement GRC in Cybersecurity
To successfully integrate GRC in cybersecurity, organizations should consider the following steps: Careful planning, strategic execution, and ongoing evaluation are needed because every organization has different needs, regulatory landscapes, and risk tolerances.
1. Assessing Current Policies and Risks
Before starting the GRC framework, you should examine your organization’s policies, procedures, and risk posture to find holes, duplicates, and areas where regulations are not being followed. For example, are your cybersecurity protocols in line with regulations? Are there risks that cannot be fixed in your operations? A thorough risk assessment reveals weaknesses that need immediate attention.
2. Setting Clear Governance Structures
Governance is the most crucial part of GRC. Make sure everyone in the organization knows their roles, responsibilities, and who is responsible for what. Using cross-functional committees or a Chief Risk Officer, leadership can set strategic goals and monitor compliance.
3. Choosing the Right Frameworks and Tools
Depending on your industry and compliance needs, choose frameworks like ISO 27001, NIST Cybersecurity Framework, or COBIT to manage risks and ensure compliance. Beyond frameworks, advanced technology tools are essential for smooth operations. Choose systems that interact with your infrastructure and offer sophisticated monitoring, reporting, and automation. Your team can focus on strategic goals using risk assessment, compliance tracking, and governance management tools that simplify and improve accuracy and efficiency.
These frameworks and tools help your organization manage cybersecurity governance, risk, and compliance. This proactive method protects against cyberattacks and meets changing regulatory requirements.
Tools and Technologies for GRC Implementation
GRC technologies are vast and changing quickly to keep up with cyber threats. Using the right tools and platforms makes GRC processes more efficient and ensures they can be scaled up and managed accurately.
Software Solutions Tailored for GRC
Modern GRC platforms like RSA Archer, MetricStream, and LogicGate centralize data to track risks, monitor compliance, and generate useful reports in real time. Make sure your solution can be customized to your industry and grow with your business.
Automation for Streamlined Processes
Automation tools make complicated tasks like tracking compliance, assessing risk, and responding to incidents easier for big businesses. Imagine a system that reports non-compliance issues immediately or sets up regular audits on its own.
Reporting and Analytics for Informed Decision-Making
Analytics tools in GRC platforms provide detailed information about risk patterns, compliance trends, and governance metrics. Dashboards with visualized data help decision-makers identify urgent issues. AI-powered predictive analytics can even predict potential risks, allowing organizations to address them before they worsen.
As cybersecurity landscapes change, adding these technologies to your GRC framework can keep your firm adaptable, up-to-date, and robust.
Challenges in GRC Implementation
Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) frameworks in cybersecurity improve security, operations, and risk, but organizations often face a maze of issues that can derail even the best-laid plans. Knowing these issues is key to solving them and ensuring that GRC practices are not only implemented but also become part of an organization’s culture.
Common Barriers to Effective GRC Practices
Organizational resistance, which is hard to hear but real, is the biggest problem with GRC implementation. Employees who do not want to change, do not know how important GRC is, or are stuck in old ways of doing things may resist. Leaders may also be hesitant because they see GRC as a cost center instead of a strategic investment.
It is also difficult to get money, competent staff, and decent technology. Smaller organizations may struggle to afford robust GRC solutions, and larger companies may struggle to locate professionals to understand complex frameworks.
In addition, regulations are difficult to understand. From GDPR and HIPAA to ISO 27001 and NIST, organizations must follow a huge number of standards, each with its own specifics and overlapping requirements. For many, the sheer number of legal and regulatory duties is too much to handle, resulting in broken or unfinished GRC implementations.
Overcoming GRC Challenges
This may seem difficult, but an organized and planned approach can help firms overcome these issues and effectively employ GRC standards.
1. Foster Leadership Buy-In:
The first and most important step is convincing senior leadership that GRC is a strategic imperative, not just an operational necessity. Create a strong business case that highlights the real benefits of GRC, such as reduced cyber risks, better compliance, and possible cost savings from avoiding regulatory fines. Use real-life examples to demonstrate how competitors have used GRC to gain a competitive edge.
2. Invest in Awareness and Training:
Inform and involve employees and partners in GRC strategy development through workshops, engaging materials, and team participation. Informed and included employees are more likely to accept changes.
3. Leverage Scalable Tools and Technologies:
A good GRC platform has automation, easy-to-use dashboards, and connection with other systems to reduce manual effort and improve risk management.
4. Simplify Compliance Processes:
Break down complicated laws into simpler components and create a compliance roadmap that prioritizes requirements and uses modest stages to achieve full compliance. This keeps teams calm and assures consistent progress.
5. Strengthen Collaboration Across Departments:
To improve GRC, form cross-functional teams with IT, legal, finance, and operations professionals. Meet regularly and share KPIs to keep everyone informed and give everyone a sense of ownership over GRC projects.
6. Continuously Monitor and Adapt:
Organizations confront shifting rules and hazards, so examine and enhance their GRC procedures often. Use analytics and data to detect gaps and alter tactics as needed.
By facing these issues head-on, companies can turn GRC from a burden into a powerful tool that helps them grow and be resilient. The journey may be difficult, but the benefits—stronger cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency—are worth it.
Benefits of Effective GRC Practices
Complete GRC (Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance) practices can help organizations navigate today’s complex cybersecurity landscape. These benefits go beyond improving operations; they build trust and resilience in an increasingly unstable digital world.
Enhanced Security Posture
Because cyber threats change constantly, a strong GRC framework protects an organization from them by finding weaknesses and lowering risks ahead of time. This proactive approach reduces breaches and strengthens system integrity, building trust within and outside the organization.
Reduced Compliance Risks
Compliance with cybersecurity regulations is essential to avoid harsh fines, reputation damage, and operational issues. GRC practices make it easier to follow legal and regulatory requirements by building compliance into the organization’s core.
Streamlined Processes and Operational Efficiency
Modern businesses need efficiency, and GRC helps them achieve that by combining governance, risk, and compliance functions to eliminate unnecessary tasks, improve workflows, and reduce operational silos. GRC lets businesses work with precision and speed by letting all departments communicate risks and follow the same rules.
Improved Trust with Stakeholders and Customers
GRC practices help businesses earn and maintain customer, partner, and regulator trust by showing they care about data protection, risk reduction, and compliance. This trust leads to loyal customers, stronger partnerships, and a market edge.
To conclude, good GRC practices are required for operations and a strategic asset. They improve security, process efficiency, and trust to help organizations thrive in the complex digital age.
GRC Use Cases
Industry-Specific Applications of GRC in Cybersecurity
Healthcare, finance, and government are some of the first and most important digital industries, and they hold a lot of sensitive data. Each has its own cybersecurity issues, so GRC frameworks are crucial.
Healthcare:
The stakes are always high in healthcare. Cybercriminals profit from HIPAA-protected patient data. GRC frameworks simplify compliance and risk management, letting hospitals and clinics focus on treatment. Mid-sized hospitals may have antiquated, ransomware-vulnerable technology. A GRC solution may consolidate compliance, automate risk assessments, and protect vital infrastructure from threats.
Finance:
The finance sector is closely monitored by regulatory organizations. Phishing and sophisticated insider threats demand effective risk management. A global bank fighting fraud can align internal controls with SOX and Basel III using a GRC architecture. Prioritizing real-time threat detection ensures compliance and customer trust.
Government:
Nation-state actors threaten government agencies that store confidential and citizen data. A government agency employing GRC can comply with NIST and better identify and mitigate risks across sprawling IT infrastructures. Public health agencies must secure systems and comply with changing laws to manage risk.
Each industry shows that a well-tailored GRC approach extends beyond compliance to protect against industry-specific issues and strengthen cybersecurity.
Case Studies: Real-World Success Stories
GRC case stories demonstrate how its principles may transform an organization’s safety from reactive to proactive.
Case Study 1: A Regional Hospital’s Journey to Cybersecurity Excellence
As ransomware threats increased, this hospital implemented an integrated GRC solution to fix their weaknesses. Using automated compliance tracking and ongoing risk assessment, they cut their attack surface by 40% in one year and achieved full HIPAA compliance, earning patient and stakeholder trust.
Case Study 2: A Global Bank Battling Fraud with GRC
As fraud cases increased, a global bank implemented a GRC platform across all of its operations. The results were amazing: the bank cut fraud detection time in half while meeting international compliance standards. The centralized risk management dashboard gave the team a full picture of vulnerabilities allowing them to act quickly.
Case Study 3: Government Agency Securing Citizen Data
A government agency with sensitive citizen data faced increasing cyber attacks on its legacy systems. To protect themselves, they implemented a GRC framework based on NIST guidelines that improved defences, streamlined incident response protocols and reduced compliance gaps. Within two years, their cybersecurity risk rating dropped by 35%, boosting public confidence.
These examples show that GRC is more than a compliance tool; it transforms organisations to predict, address and overcome cybersecurity issues, regardless of size or industry.
How to Implement a GRC Strategy
Building a Customized GRC Framework
Each organization’s Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) strategy must be tailored to its size, structure, and industry challenges. For example, a small tech startup may focus on agile risk management processes, while a multinational healthcare provider may focus on strict compliance to meet regulations.
First, assess your organization’s budget. Can you afford cutting-edge GRC tools, or will you start with basic frameworks? Next, assess your risk profile. High-risk industries, like finance, need strong tools to deal with complex threats, while other industries may not have as much at stake. Finally, think of your GRC framework as a living thing that can adapt, grow, and change as your organization or regulations do.
Customization goes further. Automating repetitive compliance tasks frees up resources so teams can focus on high-priority risks. Including stakeholders from across departments ensures that the GRC framework is part of the whole organization.
Measuring the Effectiveness of GRC Strategies
Setting metrics and KPIs to measure your GRC framework’s effectiveness is like sailing without a compass—you will not know where you are going or what to expect. What does success look like? Shorter incident response times? Higher compliance scores? The metrics should match your organization’s goals.
For instance, a real-time compliance dashboard could display audit readiness scores, flagged risks, and resolution timelines. Tools like Tableau or Power BI can turn raw data into actionable insights that help leaders track progress and identify weaknesses.
Do not stop collecting data—review these KPIs regularly to make strategy changes. If risks or compliance gaps remain, re-calibrate. Good GRC is an ever-evolving process that improves.
GRC strategy building and measurement requires careful preparation and adaptability. By adjusting the framework to your organization’s needs and using the correct data and technologies, you can construct a robust, compliant, and forward-looking corporation.
Conclusion
Governance sets a clear strategic direction, risk management finds and fixes vulnerabilities, and compliance protects organizations from regulatory pitfalls. These three areas make up a strong triad that is necessary for resilience in the digital age.
Companies that want to stay ahead of cyberattackers must use GRC. A well-implemented GRC framework protects against immediate threats and strengthens an organization’s foundation, ensuring long-term stability and trust from stakeholders, customers, and regulators.
Companies must act now to make GRC a strategic part of their cybersecurity. Spend money on the right tools, encourage accountability, and prioritize continuous improvement. By doing so, your company will lower its risks and become a cybersecurity leader.
FAQs
What are the best GRC frameworks for cybersecurity?
Some of the best GRC frameworks for cybersecurity include:
ISO 27001: Focused on information security management.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Offers a flexible approach to managing and reducing risks.
COBIT: Ideal for aligning IT governance with organizational objectives.
These frameworks can be tailored to suit specific industries and regulatory needs, providing a solid foundation for cybersecurity governance.
What tools are available for GRC in cybersecurity?
Several tools are available to streamline GRC processes, such as:
RSA Archer: For risk and compliance management.
LogicGate: Offers flexibility for building custom workflows.
OneTrust: Specializes in privacy, compliance, and risk solutions.
These tools automate compliance tracking, risk assessments, and reporting, making it easier for organizations to manage their cybersecurity efforts efficiently.
